Introduction:
Three drug regimen using bortezomib (V), lenalidomide (R), and dexamethasone (d) is a standard first-line treatment modality for multiple myeloma (MM). If compared to bortezomib that can cause neurotoxicity, ixazomib is an oral proteasome inhibitor (PI) with markedly lower chances of neurotoxicity. Ixazomib (I) use showed favorable results in both newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) and relapsed refractory MM (RRMM). This systemic review compares the efficacy and safety outcomes of IRd with VRd in MM patients.
Methods:
We performed a comprehensive literature search on PubMed, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov on June 9, 2020. We used the MeSH terms for 'multiple myeloma', 'ixazomib', 'bortezomib', 'dexamethasone', 'lenalidomide', and their associated keywords. The search yielded 1117 articles. Screening and data extraction were done following PRISMA guidelines. After excluding case reports, case series, observational studies, review articles, meta-analysis, and retrospective studies, 18 clinical trials (n=2295) were shortlisted of which six assessed IRd and twelve assessed VRd.
Results:
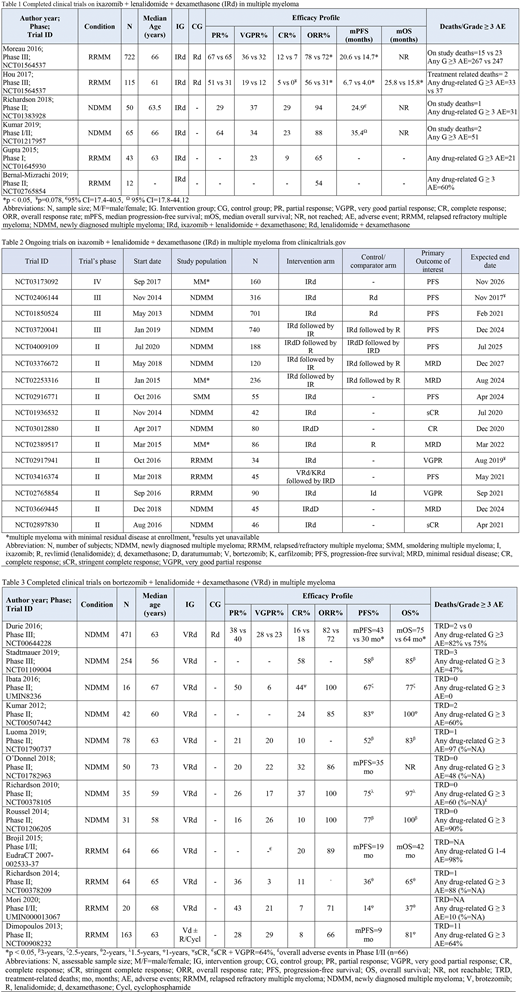
No direct comparison trial between IRd and VRd was found. Total 1007 patients were evaluable who received IRd (Table 1). Among them 892 had RRMM and 115 had NDMM. Moreover, total 1288 evaluable patients received VRd where 977 had NDMM and 311 had RRMM (Table 3).
IRd arm results
Among 892 RRMM patients received IRd, Gupta et al. (2015, n=43) reported an overall response rate (ORR) of 65% with 23% achieving a very good partial response (VGPR) and 9% achieving complete response (CR). In TOURMALINE-MM1 Study by Moreau et al. (2016, n=722), authors reported the median progression-free survival (mPFS) as 20.6 months with IRd. The ORR was 78% (95% CI 74-83). Hou et al. (2017, n=115) reported mPFS of 6.7 with IRd. After a median follow-up of 20.2 months, the median overall survival (mOS) was reported to be 25.8 months. The ORR was 56% (95% CI 42-69). 115 NDMM patients received IRd in two clinical tials. Richardson et al. (2018, n=50) in a phase II trial reported an ORR of 94% (95% CI 83-99) with 29% CR and 37% VGPR. The mPFS was 24.9 months (95% CI 17.4-40.5) and 3-year OS was 90% in the intention-to-treat analysis. Kumar et al. (2019, n=65) reported ORR of 88% (CR=23%, VGPR=34%, PR=64%). The mPFS of 35.4 months (95% CI 17.8-44.12) slightly better than the previous study. The mOS was not reached in either of the trials. Any drug-related grade ≥ 3 adverse events were reported in 50% to 80% of participants receiving IRd but were manageable with prompt intervention.
VRd arm results
NDMM patients, in a phase III trial by Durie et al. (2016, n=471) achieved ORR of 82% (PR=38%, VGPR=28% and CR=16%) with VRd. The mPFS was 43 months and mOS was 75 months, both significantly better than control. Stadtmauer et al. (2019, n=254) results were similar as well with 3-year PFS and OS as 58% and 85% respectively. Kumar et al. (2012, n=42) had a 1-year OS of 100% and PFS of 83%. O'Donnel et al. (2018, n=50) achieved mPFS of 35 months while mOS could not be reached. Luoma et al. (2019, n=78) achieved a 3-year PFS of 52% while OS of 83%. Among the 311 patients who had RRMM, Brojil et al. (2015, n=64) in phase I/II study showed ORR of 89% but mPFS and mOS were limited to 19 and 42 months respectively. In Richardson et al. (2014, n=64) 2-year PFS=36% and OS=65%. Mori et al. (2020, n=68) reported ORR=71% largely driven by PR of 43%. 1-year PFS and OS were 14% and 37% respectively. The toxicity profile with VRd was mostly mild and manageable except for severe neurotoxicity.
Conclusion:
Based on the data, IRd and VRd combinations have shown comparable efficacy and safety outcomes in MM patients. IRd based all-oral regimen is showing favorable outcomes, especially in RRMM patients. Future trials to compare IRd vs VRd are recommended for NDMM and RDMM patients.
Anwer:Incyte, Seattle Genetics, Acetylon Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie Pharma, Astellas Pharma, Celegene, Millennium Pharmaceuticals.: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.